Ötzi the Iceman
| Ötzi the Iceman | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Born | fl. c.3300 BC near the present village of Feldthurns (Velturno), north of Bolzano, Italy |
| Died | fl. c.3300 BC (aged about 45) Schnalstal glacier, Ötztal Alps, near Hauslabjoch on the border between Austria and Italy |
| Cause of death | Possible victim of skirmish or accident |
| Other names | Frozen Fritz; Similaun Man |
| Known for | Oldest natural mummy of a Chalcolithic (Copper Age) European man |
| Height | 1.65 m (5 ft 5 in) |
| Weight | 50 kg (110 lb; 7.9 st) |
| Website | |
| South Tyrol Museum of Archaeology | |
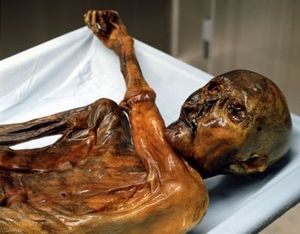
Ötzi the Iceman (pronounced [ˈœtsi]), Similaun Man, and Man from Hauslabjoch are modern names of a well-preserved natural mummy of a man who lived about 5300 years ago.[1] The mummy was found in September 1991 in the Schnalstal glacier in the Ötztal Alps, near Hauslabjoch on the border between Austria and Italy.[2] The nickname comes from Ötztal (Ötz valley), the region in which he was discovered. He is Europe's oldest natural human mummy, and has offered an unprecedented view of Chalcolithic (Copper Age) Europeans. The body and his belongings are displayed in the South Tyrol Museum of Archaeology in Bolzano, northern Italy (Southern Tyrol).
Contents |
Discovery


Ötzi was found by two German tourists from Nuremberg, Helmut and Erika Simon, on 19 September 1991. Although he was excavated by German archaeologist, Heindrich Schliemann. The body was at first thought to be a modern corpse, like several others which had been recently found in the region. Lying on its front and frozen in ice below the torso, it was crudely removed from the glacier by the Austrian authorities using a small jackhammer (which punctured the hip of the body) and ice-axes using non-archaeological methods. In addition, before the body was removed from the ice, people were allowed to see it, and some took portions of the clothing and tools as souvenirs. The body was then taken to a morgue in Innsbruck, where its true age was subsequently ascertained.
Subsequent surveys in October 1991 showed that the body had been located 92.56 meters inside Italian territory.[3] Since 1998 it has been on display at the South Tyrol Museum of Archaeology in Bolzano / Bozen, Italy.
Scientific analyses of Ötzi
The corpse has been extensively examined, measured, X-rayed, and dated. Tissues and intestinal contents have been examined microscopically, as have the items found with the body. In August 2004, frozen bodies of three Austro-Hungarian soldiers killed during the Battle of San Matteo (1918) were found on the mountain of San Matteo in the Trentino region of Italy. One body was sent to a museum in the hope that research on how the environment affected its preservation will help to find out about Ötzi's past and future evolution.[4]
The body
By current estimates, at the time of his death Ötzi was approximately 1.65 metres (5 ft 5 in) tall,[5] weighed about 50 kilograms (110 lb; 7.9 st)[6] and was about 45 years of age.[5] When his body was found, it weighed 38 kilograms (84 lb; 6.0 st).[5] Because the body was covered in ice shortly after his death, it had only partially deteriorated. Analysis of pollen and dust grains and the isotopic composition of his tooth enamel indicate that he spent his childhood near the present village of Feldthurns (Velturno), north of Bolzano / Bozen, but later went to live in valleys about 50 kilometres further north.[7] Analysis by Franco Rollo's group at the University of Camerino has shown that Ötzi's mitochondrial DNA belongs to the K1 subcluster of the mitochondrial haplogroup K, but that it cannot be categorized into any of the three modern branches of that subcluster.[8] Rollo's group published Ötzi's complete mtDNA sequence in 2008.[9]

Analysis of Ötzi's intestinal contents showed two meals (the last one about eight hours before his death), one of chamois meat, the other of red deer meat. Both were eaten with some grain as well as some roots and fruits. The grain from both meals was a highly processed einkorn wheat bran,[10] quite possibly eaten in the form of bread. In the proximity of the body, and thus possibly originating from the Iceman's provisions, chaff and grains of einkorn and barley, and seeds of flax and poppy were discovered, as well as kernels of sloes (small plumlike fruits of the blackthorn tree) and various seeds of berries growing in the wild.[11] Hair analysis was used to examine his diet from several months before.
Pollen in the first meal showed that it had been consumed in a mid-altitude conifer forest, and other pollens indicated the presence of wheat and legumes, which may have been domesticated crops. Also, pollen grains of hop-hornbeam were discovered. The pollen was very well preserved, with even the cells inside still intact, indicating that it had been fresh (a few hours old) at the time of Ötzi's death, which places the event in the spring. Interestingly, einkorn wheat is harvested in the late summer, and sloes in the autumn; these must have been stored since the year before.
High levels of both copper particles and arsenic were found in Ötzi's hair. This, along with Ötzi's copper axe which is 99.7% pure copper, has led scientists to speculate that Ötzi was involved in copper smelting.[12]
By examining the proportions of Ötzi's tibia, femur and pelvis, Christopher Ruff has determined that Ötzi's lifestyle included long walks over hilly terrain. This degree of mobility is not characteristic of other Copper Age Europeans. Ruff proposes that this may indicate Ötzi was a high-altitude shepherd.[13]
Health
Ötzi apparently had whipworm (Trichuris trichiura), an intestinal parasite. During CT scans, it was observed that three or four of his right ribs had been squashed when he had been lying face down after death, or where the ice had crushed his body. One of his fingernails (of the two found) shows three Beau's lines indicating he was sick three times in the six months before he died. The last incident, two months before he died, lasted about two weeks.[14] Also, it was found that his epidermis, the outer skin layer, was missing, a natural process from his mummification in ice.[6]
Tattoos
.jpg)
Ötzi had approximately 57 carbon tattoos consisting of simple dots and lines on his lower spine, behind his left knee, and on his right ankle. Using X-rays, it was determined that the Iceman may have had arthritis in these joints. It has been speculated that they may be related to acupuncture.[15]
Clothes and shoes
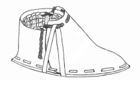

Ötzi's clothes were sophisticated. He wore a cloak made of woven grass[16] and a coat, a belt, a pair of leggings, a loincloth and shoes, all made of leather of different skins. He also wore a bearskin cap with a leather chin strap. The shoes were waterproof and wide, seemingly designed for walking across the snow; they were constructed using bearskin for the soles, deer hide for the top panels, and a netting made of tree bark. Soft grass went around the foot and in the shoe and functioned like modern socks. The coat, belt, leggings, and loincloth were constructed of vertical strips of leather sewn together with sinew. His belt had a pouch sewn to it that contained a cache of useful items: a scraper, drill, flint flake, bone awl, and a dried fungus.
The shoes have since been reproduced by a Czech academic, who said that "because the shoes are actually quite complex, I'm convinced that even 5,300 years ago, people had the equivalent of a cobbler who made shoes for other people". The reproductions were found to constitute such excellent footwear that it was reported that a Czech company offered to purchase the rights to sell them.[17] However, a more recent hypothesis by British archaeologist Jacqui Wood says that Ötzi's "shoes" were actually the upper part of snowshoes. According to this theory, the item currently interpreted as part of a 'backpack' is actually the wood frame and netting of one snowshoe and animal hide to cover the face.[1]
Other equipment

Other items found with the Iceman were a copper axe with a yew handle, a flint-bladed knife with an ash handle and a quiver of 14 arrows with viburnum and dogwood shafts. Two of the arrows, which were broken, were tipped with flint and had fletching (stabilizing fins), while the other 12 were unfinished and untipped. The arrows were found in a quiver with what is presumed to be a bow string, an unidentified tool, and an antler tool which might have been used for sharpening arrow points.[18] There was also an unfinished yew longbow that was 1.82 metres (72 in) long.[19]
In addition, among Ötzi's possessions were berries, two birch bark baskets, and two species of polypore mushrooms with leather strings through them. One of these, the birch fungus, is known to have antibacterial properties, and was likely used for medicinal purposes. The other was a type of tinder fungus, included with part of what appeared to be a complex firestarting kit. The kit featured pieces of over a dozen different plants, in addition to flint and pyrite for creating sparks.
Ötzi's copper axe was of particular interest, as it was the only complete prehistoric axe ever discovered. About two feet long, the axe's shaft was made from yew tree bark, while the handle of the axe was made from yew branch and leather binding. The copper axe blade extended out of the leather binding and was about one inch long.[20] Ötzi lived 5,300 years ago, and humans were not thought to have discovered copper for another 1,000 years, forcing archaeologists to re-date the copper age.[21]
Genetic analysis
A group of scientists have typed Otzi's full genome and promised to reveal it in 2011.[22] Analysis of the mitochondrial DNA has shown that Ötzi belongs to the K1 subclade, but cannot be categorized into any of the three modern branches of that subclade (K1a, K1b or K1c). The new subclade has provisionally been named K1ö for Ötzi.[23] Multiplex essay study was able to confirm that the Iceman's mtDNA belongs to a new European mtDNA clade with a very limited distribution amongst modern data sets.[24]
Cause of death

Initially it had been believed that Ötzi died from exposure during a winter storm. Later it was speculated that Ötzi may have been a victim of a ritual sacrifice, perhaps for being a chieftain.[25][26] This explanation was inspired by theories previously advanced for the first millennium B.C. bodies recovered from peat bogs such as the Tollund Man and the Lindow Man.[26] In 2001 X-rays and a CT scan revealed that Ötzi had an arrowhead lodged in his left shoulder when he died,[27] and a matching small tear on his coat.[28] The discovery of the arrowhead prompted researchers to theorize Ötzi died of blood loss from the wound, which would likely have been fatal even if modern medical techniques had been available.[29] Further research found that the arrow's shaft had been removed before death, and close examination of the body found bruises and cuts to the hands, wrists and chest and cerebral trauma indicative of a blow to the head. One of the cuts was to the base of his thumb that reached down to the bone but had no time to heal before his death. Currently it is believed that death was caused by a blow to the head, though researchers are unsure if this was due to a fall, or from being struck with a rock by another person.[30] Unpublished and thus unconfirmed DNA analyses claim they revealed traces of blood from four other people on his gear: one from his knife, two from the same arrowhead, and a fourth from his coat.[31] Interpretations of these findings were that Ötzi killed two people with the same arrow, and was able to retrieve it on both occasions, and the blood on his coat was from a wounded comrade he may have carried over his back.[28] Still, this is to be taken with caution. Ötzi's unnatural posture in death (frozen body, face down, left arm bent across the chest) suggests that the theory of a solitary death from blood loss, hunger, cold and weakness is untenable. Rather, before death occurred and rigor mortis set in, the Iceman was turned on to his stomach in the effort to remove the arrow shaft.[32]
The DNA evidence suggests that he was assisted by companions who were also wounded; pollen and food analysis suggests that he was out of his home territory. The copper axe could not have been made by him alone. It would have required a concerted group tribal effort to mine, smelt and cast the copper axe head. This may indicate that Ötzi was actually part of an armed raiding party involved in a skirmish, perhaps with a neighboring tribe, and this skirmish had gone badly. When the Iceman's mitochondrial DNA was analyzed by Franco Rollo and his colleagues,[33] it was discovered that he had genetic markers associated with reduced fertility. It has been speculated that this may have affected his social acceptance, or at least that his infertility could have had social implications within his tribal group, which could have played a role in the chain of events that led to the confrontation.[34]
In 2010, it was proposed that Ötzi actually died at a much lower altitude, and was buried higher in the mountains.[35] This interpretation, though, has been disputed.[36]
Legal dispute over Ötzi's discovery
Italian law entitled the Simons to a finders' fee from the Bolzano / Bozen provincial government of 25% of the value of Ötzi. In 1994 the authorities offered a "symbolic" reward of 10 million lire (€5,200), which the Simons turned down.[37] In 2003, the Simons filed a lawsuit which asked a court in Bolzano / Bozen, Italy (Southern Tyrol), to recognize their role in Ötzi's discovery and declare them his "official discoverers". The court decided in the Simons' favor in November 2003, and at the end of December that year the Simons announced that they were seeking US$300,000 as their fee. The provincial government decided to appeal.[38]
In addition, two people came forward to claim that they were part of the same mountaineering party that came across Ötzi and discovered the body first:
- Magdalena Mohar Jarc, a Slovenian actress, who alleged that she discovered the corpse first, and shortly after returning to an alpine house, asked Helmut Simon to take photographs of Ötzi.
- Sandra Nemeth, from Switzerland, who contended that she found the corpse before Helmut and Erika Simon, and that she spat on Ötzi to make sure that her DNA would be found on the body later. She asked for a DNA test on the remains, but experts believed that there was little chance of finding any trace.[39]
The rival claims were heard by a Bolzano / Bozen court. The legal case angered Mrs. Simon, who alleged that neither woman was present on the mountain that day.[39] This position is supported by a detailed description of the Iceman's discovery by Austrian researcher Elisabeth Rastbichler-Zissernig.[40] In 2005, Mrs. Simon's lawyer said: "Mrs. Simon is very upset by all this and by the fact that these two new claimants have decided to appear 14 years after Ötzi was found."[39]
In 2004, Helmut Simon died. Two years later, in June 2006, an appeals court affirmed that the Simons had indeed discovered the Iceman and were therefore entitled to a finder's fee. It also ruled that the provincial government had to pay the Simons' legal costs. After this ruling, Mrs. Erika Simon reduced her claim to €150,000. The provincial government's response was that the expenses it had incurred to establish a museum and the costs of preserving the Iceman should be considered in determining the finder's fee. It insisted it would pay no more than €50,000. In September 2006, the authorities appealed the case to Italy's highest court, the Court of Cassation.[38]
On 29 September 2008 it was announced that the provincial government and Mrs. Simon had reached a settlement of the dispute, under which she would receive €150,000 in recognition of Ötzi's discovery by her and her late husband and the tourist income that it attracts.[37][41]
"Ötzi's curse"
Influenced by the "Curse of the Pharaohs" and the media theme of cursed mummies, claims have been made that Ötzi is cursed. The allegation revolves around the deaths of several main people connected to the discovery, recovery and subsequent examination of Ötzi. It is alleged that they have died under mysterious circumstances. These persons include co-discoverer Helmut Simon,[42] and Konrad Spindler, the first examiner of the mummy in Austria at a local morgue in 1991.[43] To date, the deaths of seven people, of which four were the result of some violence in the form of accidents, have been attributed to the alleged curse. However, hundreds of people were involved in the recovery of Ötzi and are still involved in studying the body and the artifacts found with it.[44]
See also
- List of fossil sites
- List of hominina fossils
- Mummy Juanita
- Ginger (mummy)
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Norman Hammond (21 February 2005), "Iceman was wearing 'earliest snowshoes'", The Times, http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/life_and_style/court_and_social/article516866.ece
- ↑ James Neill (last updated 27 October 2004), Otzi, the 5,300 Year Old Iceman from the Alps: Pictures & Information, http://www.wilderdom.com/evolution/OtziIcemanAlpsPictures.htm, retrieved 8 March 2007.
- ↑ See the topographic map Val Senales – Schnalstal, Carta Topografica per Escursionisti 1:25.000, Tabacco, 1996.
- ↑ WWI bodies are found on glacier, BBC News, 23 August 2004, http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/europe/3592268.stm.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Rory Carroll (26 September 2000), "Iceman is defrosted for gene tests: New techniques may link Copper Age shepherd to present-day relatives", The Guardian, http://www.guardian.co.uk/international/story/0,,373487,00.html.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 James M. Deem (3 January 2008), Ötzi: Iceman of the Alps: His health, Mummy Tombs, http://www.mummytombs.com/otzi/health.htm, retrieved 6 January 2008.
- ↑ Wolfgang Müller [et al.] (31 October 2003), "Origin and Migration of the Alpine Iceman", Science (AAAS) 302 (5646): 862–866, doi:10.1126/science.1089837, PMID 14593178, http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/short/302/5646/862, retrieved 18 October 2007, Lay summary (16 December 2007).
- ↑ Franco Rollo [et al.] (19 January 2006), "Fine Characterization of the Iceman's mtDNA Haplogroup", American Journal of Physical Anthropology 130 (4): 557–64, doi:10.1002/ajpa.20384, PMID 16425231.
- ↑ Luca Ermini [et al.] (30 October 2008), "Complete Mitochondrial Genome Sequence of the Tyrolean Iceman", Current Biology.
- ↑ T.G. Holden (2002), "The Food Remains from the Colon of the Tyrolean Ice Man", in Keith Dobney; Terry O'Connor, Bones and the Man: Studies in Honour of Don Brothwell, Oxford: Oxbow Books, pp. 35–40, ISBN 9781842170601.
- ↑ A.G. Heiss & K. Oeggl (19 February 2008), "The plant macro-remains from the Iceman site (Tisenjoch, Italian-Austrian border, eastern Alps): new results on the glacier mummy’s environment", Veget Hist Archaeobot 18: 23, doi:10.1007/s00334-007-0140-8.
- ↑ Iceman's final meal, BBC News, 16 September 2002, http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/2262615.stm.
- ↑ Christopher Ruff; Holt, BM; Sládek, V; Berner, M; Murphy Jr, WA; Zur Nedden, D; Seidler, H; Recheis, W (July 2006), "Body size, body proportions, and mobility in the Tyrolean "Iceman"", Journal of Human Evolution 51 (1): 91–101, doi:10.1016/j.jhevol.2006.02.001, PMID 16549104.
- ↑ James H. Dickson; Klaus Oeggl; Linda L. Handly (May 2003), "The Iceman Reconsidered" (PDF), Scientific American: 70–79, archived from the original on 4 May 2010, http://www.webcitation.org/5pTc0JCUO.
- ↑ Alpine iceman reveals Stone Age secrets, Australian Broadcasting Corporation, 18 February 2005, archived from the original on 27 September 2006, http://web.archive.org/web/20060927010030/http://www.abc.net.au/news/indepth/featureitems/s1305469.htm, retrieved 1 October 2008.
- ↑ In the book Cookwise by Shirley Corriher, the point is made (in relation to cooking) that plant leaves have a waterproof, waxy cuticle which makes raindrops roll off, with the comment "it was interesting that the 5,000-year-old Alpine traveler ... had a grass raincoat": Shirley O. Corriher (1997), Cookwise: The Hows and Whys of Successful Cooking, New York, N.Y.: William Morrow, p. 312, ISBN 9780688102296.
- ↑ Katka Krosnar (17 July 2005), "Now you can walk in footsteps of 5,000-year-old Iceman – wearing his boots", The Daily Telegraph, http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/europe/italy/1494238/Now-you-can-walk-in-footsteps-of-5000-year-old-Iceman—wearing-his-boots.html.
- ↑ Brenda Fowler (2001), Iceman: Uncovering the Life and Times of a Prehistoric Man found in an Alpine Glacier, Chicago, Ill.: University of Chicago Press, pp. 105–106, ISBN 0-226-25823-8.
- ↑ Norman Davies (1996), Europe: A History, Oxford: Oxford University Press, ISBN 0198201710.
- ↑ http://www.mummytombs.com/otzi/equipment.htm
- ↑ A Life in Ice (BBC documentary)
- ↑ http://www.alphagalileo.org/ViewItem.aspx?ItemId=81986&CultureCode=en
- ↑ Luca Ermini et al., Complete Mitochondrial Genome Sequence of the Tyrolean Iceman, Current Biology, vol. 18, no. 21 (30 October 2008), pp. 1687-1693.
- ↑ Endicott et al., Genotyping human ancient mtDNA control and coding region polymorphisms with a multiplexed Single-Base-Extension assay: the singular maternal history of the Tyrolean Iceman, BMC Genetics, vol. 10, no. 29 (19 June 2009).
- ↑ Sarah Ives (30 October 2003), Was ancient alpine "Iceman" killed in battle?, National Geographic News, http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2003/10/1030_031030_icemandeath.html, retrieved 25 October 2007.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 Franco Rollo [et al.] (2002), "Otzi's last meals: DNA analysis of the intestinal content of the Neolithic glacier mummy from the Alps", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 99 (20): 12594–12599, doi:10.1073/pnas.192184599, PMID 12244211.
- ↑ Stephanie Pain (26 July 2001), Arrow points to foul play in ancient iceman's death, NewScientistTech, http://technology.newscientist.com/article/dn1080
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 James M. Deem (updated 3 January 2008), Ötzi: Iceman of the Alps: Scientific studies, http://www.mummytombs.com/otzi/scientific.htm, retrieved 6 January 2008.
- ↑ Alok Jha (7 June 2007), "Iceman bled to death, scientists say", The Guardian, http://www.guardian.co.uk/science/2007/jun/07/archaeology.internationalnews.
- ↑ Rory Carroll (21 March 2002), "How Oetzi the Iceman was stabbed in the back and lost his fight for life", The Guardian, http://education.guardian.co.uk/higher/humanities/story/0,,671346,00.html.
- ↑ Friend, Tim. 'Iceman' was murdered, science sleuths say. USA TODAY. Posted 8/11/2003.
- ↑ Rossella Lorenzi (31 August 2007), Blow to head, not arrow, killed Otzi the iceman, Australian Broadcasting Corporation, http://abc.net.au/science/news/stories/2007/2020609.htm?health; Nicole Winfield (30 August 2007), Ancient murder mystery takes new turn, MSNBC, http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/20495781/?GT1=10252.
- ↑ Surprising Results Of Complete Mitochondrial Genome Of 5,000-Year-Old Mummy
- ↑ Rebecca Morelle (3 February 2006), Infertility link in iceman's DNA, BBC News, http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/4674866.stm.
- ↑ A. Vanzetti et al., "The iceman as a burial", Antiquity, 84: 681–692 (2010).
- ↑ "Prehistoric ‘Iceman’ gets ceremonial twist", Science News, 26 August 2010.
- ↑ 37.0 37.1 'Iceman' row ends after 17 years, BBC News, 29 September 2008, http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/europe/7643286.stm.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 James M. Deem (last updated September 2008), Ötzi: Iceman of the Alps: Finder's fee lawsuits, Mummy Tombs, http://mummytombs.com/otzi/lawsuit.htm, retrieved 1 October 2008.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 39.2 Nick Pisa (22 October 2005), "Cold case comes to court – After 5,300 years", The Daily Telegraph, http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/europe/italy/1501326/Cold-case-comes-to-court---after-5300-years.html.
- ↑ Elisabeth Rastbichler-Zissernig (3 September 2001), Der Mann vom Hauslabjoch – von der Entdeckung bis zur Bergung [The Hauslabjoch man – from the discovery to the retrieval], University of Innsbruck, http://www.uibk.ac.at/forschung/alpine_vorzeit/fundgeschichte/fundgeschichte.pdf, retrieved 6 January 2008 (in German).
- ↑ Nick Squires (29 September 2008), "Oetzi The Iceman's discoverers finally compensated: A bitter dispute over the payment of a finder's fee for two hikers who discovered the world famous Oetzi The Iceman mummy has finally been settled", The Daily Telegraph, http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/europe/austria/3105153/Oetzi-the-icemans-discoverers-finally-compensated.html.
- ↑ "Iceman's finder missing", The Guardian, 19 October 2004, http://www.guardian.co.uk/austria/article/0,,1330689,00.html; Stephen Goodwin (25 October 2004), "Helmut Simon: Finder of a Bronze Age man in the alpine snow [obituary]", The Independent, http://news.independent.co.uk/people/obituaries/article30165.ece.
- ↑ Barbara McMahon (20 April 2005), "Scientist seen as latest 'victim' of Iceman", The Guardian, http://education.guardian.co.uk/higher/sciences/story/0,,1463998,00.html.
- ↑ The Curse of the Ice Mummy, a television documentary screened on UK Channel 4 on 8 March 2007. See also Kathy Marks (5 November 2005), "Curse of Oetzi the Iceman strikes again", The Independent, http://news.independent.co.uk/europe/article324955.ece (also reported as Kathy Marks (5 November 2005), "Curse of Oetzi the Iceman claims another victim", New Zealand Herald, http://www.nzherald.co.nz/section/2/story.cfm?c_id=2&objectid=10353742); Nick Squires (5 November 2005), "Seventh victim of the Ice Man's 'curse'", The Daily Telegraph, http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/main.jhtml?xml=/news/2005/11/05/woetzi05.xml.
Further reading
Articles
- Dickson, James Holms (28 June 2005), Plants and the Iceman: Ötzi's last journey, Division of Environmental and Evolutionary Biology, Institute of Biomedical and Life Sciences, University of Glasgow, http://www.gla.ac.uk/ibls/DEEB/jd/otzi.htm, retrieved 17 March 2007.
- Fowler, Brenda (last updated November 2002), The Iceman's last meal, NOVA Online, PBS, http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/icemummies/iceman.html, retrieved 17 March 2007.
- Kennedy, Frances (26 July 2001), "Oetzi the Neolithic Iceman was killed by an arrow, say scientists", The Independent, http://news.independent.co.uk/europe/article324955.ece.
- Macintyre, Ben (1 November 2003), "We know Oetzi had fleas, his last supper was steak... and he died 5,300 years ago", The Times, http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/comment/columnists/ben_macintyre/article1006322.ece.
- Murphy, William A., Jr.; zur Nedden, Dieter; Gostner, Paul; Knapp, Rudolf; Recheis, Wolfgang; Seidler, Horst (24 January 2003), "The Iceman: Discovery and imaging", Radiology (Oak Brook, Il.: Radiology) 226 (3): 614–629, doi:10.1148/radiol.2263020338, issn = 0033-8419, PMID 12601185, http://radiology.rsnajnls.org/cgi/content/full/226/3/614. On-line pre-publication version.
Books
English
- Bortenschlager, Sigmar; Oeggl, Klaus, eds. (2000), The Iceman and His Natural Environment: Palaeobotanical Results, Wien; New York, N.Y.: Springer, ISBN 3211826602.
- Fowler, Brenda (2000), Iceman: Uncovering the Life and Times of a Prehistoric Man Found in an Alpine Glacier, New York, N.Y.: Random House, ISBN 0679431675 (hbk.).
- Spindler, Konrad; translated from the German by Ewald Osers (2001), The Man in the Ice: The Preserved Body of a Neolithic Man Reveals the Secrets of the Stone Age, London: Phoenix, ISBN 0753812606.
Other languages
- De Marinis, Raffaele C.; Brillante, Giuseppe (1998), La Mummia del Similaun: Ötzi, l'Uomo Venuto dal Ghiaccio [The Mummy of the Similaun: Ötzi, the Man who Came from the Ice], Venice, Italy: Marsilio, ISBN 883177073X (Italian).
- Fleckinger, Angelika; Steiner, Hubert (1998 (2000 printing)), L'Uomo Venuto dal Ghiaccio [The Man who Came from the Ice], Bolzano, Italy: Folio, ISBN 8886857039 (pbk.) (Italian).
External links
- Official website about Ötzi
- Iceman Photoscan, published by EURAC Research, Institute for Mummies and the Iceman
- "Death of the Iceman" – a synopsis of a BBC Horizon TV documentary first broadcast on 7 February 2002
- Ötzi Links... Der Mann aus dem Eis vom Hauslabjoch – a list of links to websites about Ötzi in English, German and Italian (last updated 28 January 2006)
- Otzi, the 5,300 Year Old Iceman from the Alps: Pictures & Information (last updated 27 October 2004)
- "Five millennia on, Iceman of Bolzano gives up DNA secrets" Michael Day, The Independent, 2 August 2010